Front Wing Design with CFD Adjoint Solver
- Yanhao Zhu

- 2016年5月21日
- 讀畢需時 2 分鐘
What is the the smart shape optimization tool in Ansys Fluent?
From ANSYS website:
The ANSYS smart shape optimization tool is called adjoint technology. The tool is actually a solver that uses CFD simulation results to find an optimal solution based on stated goals (reduced drag, maximized lift-over-draft ratio, reduced pressure drop, etc.). But it doesn’t stop there: It also computes how to specifically modify the design. Because it is a solver, it has many advantages:
•It directly computes which section of the design needs to be modified and how. You do not need to define any parameters.
•It directly determines a better-performing shape as well as the associated performance improvement, all without needing another CFD simulation.
•It can, in a minimal number of simulations, determine the optimal shape. At each iteration, design performance increases until the optimal design is reached.
Is it fast?
The adjoint solver determines directly how to improve performance, so there is no time wasted on trial-and-error processes. Even more time could be saved by a script utilizing a built-in mesh morpher automatically adjusting the design shape and computational mesh following the adjoint solver recommendations.
Pros & Cons
There are many ways in which benefits can be extracted from the result of adjoint solver. By reviewing the adjoint data, one will be provided guidance on where changes to the design of a system most affect performance, thereby focusing engineering resources more effectively. Going one step further, he adjoint data can be used in gradient based optimization strategy, remarkable for shape optimization.
Shortcomings? The adjustment of constants in the model is only understandable to experts; it is also very time consuming.
How to use Adjoint Solver in ANSYS FLUENT?
The process in one iteration is described as follow:
- Solve the flow problem in usual manner;
- Select some measure of performance being interest (objective function);
- Initialize the Adjoint Solver;
- Calculate the sensitivity data;
- Modify the geometry under certain constraint;
- Solve the problem in usual manner again.
Application in MRacing (FSAE) front wing design
Currently, optimizing the whole car using Adjoint Solver in FLUENT is too costly. It would take approximately one day to do one iteration and typically we need 50 or more iterations on only one subsystem of our aero package. However, it is of great use in optimization of front wing prototype, especially in 2D cases.
The geometry of prototype we use is shown as follow:
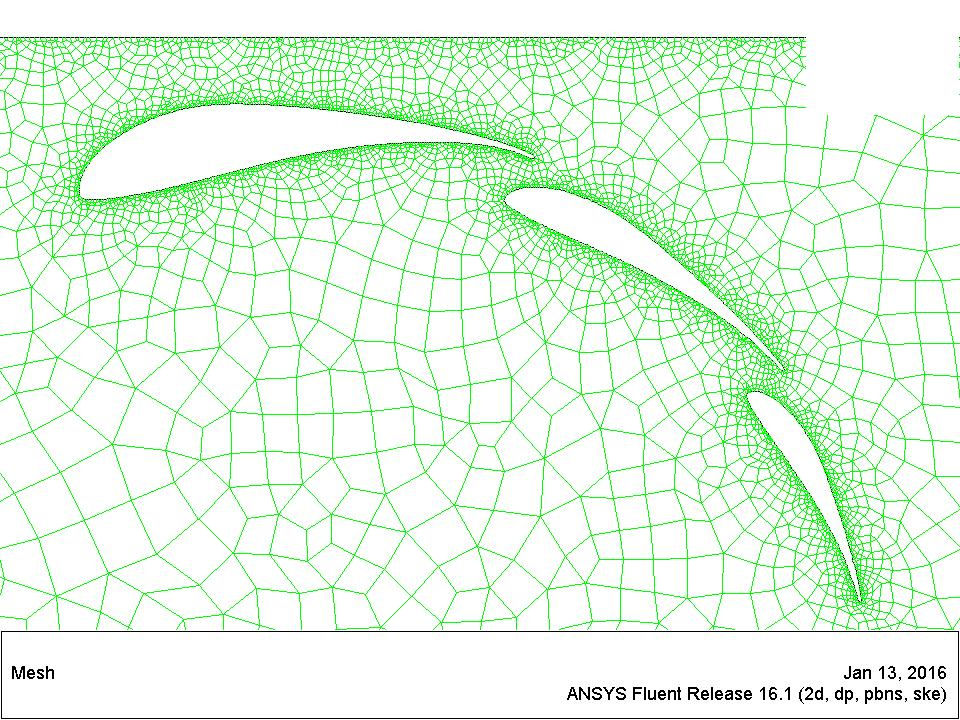
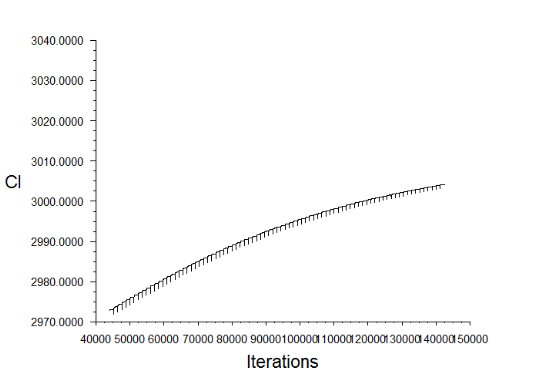
The overall lift three wings can produce is 1808 Newtons/Meter according to simulation. We set lift to be the objective function and we are going to maximize it. The middle foil is subject to change while the first and the third foil are frozen. The lift reaches 1840 Newton/Meter after 120 iteration, which is a great success. The modified geometry is shown as follow:

Given enough time, all three wings can be optimized and at least an 10 percent increase in lift is predictable. The increase of lift can be directly perceived in the change of lift versus iteration:






留言